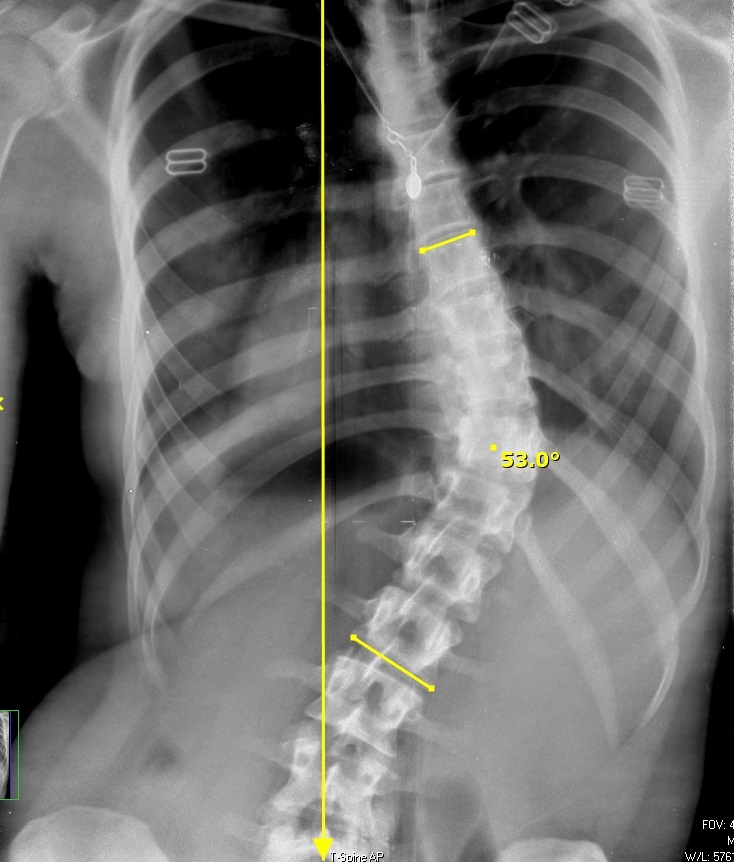
Severe Scoliosis
Severe scoliosis refers to an abnormal curvature of the spine that exceeds 50 degrees. Scoliosis is a condition characterized by lateral (sideways) curvature of the spine, which can lead to a variety of health issues. While mild cases of scoliosis often do not cause significant problems, severe scoliosis can have a substantial impact on an individual’s health and quality of life.
Causes of Severe Scoliosis
The exact cause of scoliosis is not always known, but several factors can contribute to its development, including:
- Idiopathic Scoliosis: This is the most common form of scoliosis, and it typically occurs during adolescence with no identifiable cause.
- Congenital Scoliosis: It results from abnormal spinal development before birth.
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis: Conditions such as muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, or spinal muscular atrophy can lead to scoliosis.
- Degenerative Scoliosis: It occurs due to age-related degeneration of the spine, typically in older adults.
Symptoms and Health Issues
Severe scoliosis can cause various symptoms and health issues, which may include:
- Visible Curvature: The spine may appear visibly curved, leading to an abnormal posture or asymmetry in the shoulders, hips, or rib cage.
- Back Pain: Severe scoliosis can cause back pain, particularly in the affected area of the spine and hip.
- Respiratory Problems: In many cases, the abnormal spinal curvature can restrict the space available for the lungs to expand, potentially leading to breathing difficulties.
- Limited Mobility: Severe scoliosis can affect mobility and flexibility, making it challenging to perform everyday activities comfortably.
- Digestive Issues: In many cases, moderate and severe spinal curvatures may affect the position and function of the organs in the abdomen, leading to digestive problems.
- Psychological Impact: Living with severe scoliosis can have emotional and psychological effects due to self-consciousness or body image concerns.
Treatment Options for Severe Scoliosis
The treatment approach for severe scoliosis depends on factors such as the individual’s age, the degree of curvature, and the underlying cause. While surgery is often considered for severe cases, it may not be necessary in all situations. Treatment options include:
Bracing: Bracing is commonly used in cases where the individual is still growing and the curvature is moderate. The brace helps prevent the progression of scoliosis and provides support to the spine.
Scoliosis-Specific Exercises: When it comes to severe scoliosis, it is important to approach exercise with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a qualified scoliosis specialist. Scoliosis-specific exercises aim to improve posture, spinal flexibility, and muscle strength while minimizing the progression of the spinal curvature across the lifespan. Examples of these exercises include Schroth therapy, side planks, half-moon pose, and cat-camel stretch. They are not intended to improve the curve in severe cases unless combined with other therapies such as rigid bracing, the ScoliSMART Activity Suit, or ScoliSMART BootCamp.
Surgery: There are several types of scoliosis surgery available to treat severe cases of scoliosis. Each surgical procedure aims to correct the abnormal curvature of the spine, stabilize the spine, and prevent further progression of the scoliotic curve. Examples of these surgeries include spinal fusion surgery, vertebral body tethering (VBT), anterior scoliosis correction (ASC), and ApiFix.
**It is very important to note that, in all cases of severe scoliosis, regardless of the physical treatment selected to treat the spinal curve, a comprehensive approach should be taken to evaluate the underlying factors that allowed the scoliosis to progress to that point, so that the physical treatment has a better chance of helping. After all, why wouldn’t you want to treat the underlying reasons as to why the curve started in the first place?**